 Foods and medicines can change the color of urine. But a color change also could be a sign of disease.
Foods and medicines can change the color of urine. But a color change also could be a sign of disease.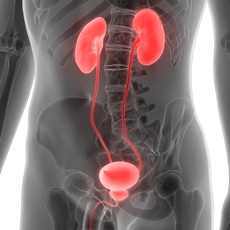 Your kidneys make urine by filtering wastes and extra water from your blood. The waste is called urea. Your blood carries it to the kidneys. From the kidneys, urine travels down two thin tubes called ureters to the bladder. The bladder stores urine until you are ready to urinate.
Your kidneys make urine by filtering wastes and extra water from your blood. The waste is called urea. Your blood carries it to the kidneys. From the kidneys, urine travels down two thin tubes called ureters to the bladder. The bladder stores urine until you are ready to urinate. The urinary system's function is to filter blood and create urine as a waste by-product. The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder and urethra.
The urinary system's function is to filter blood and create urine as a waste by-product. The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder and urethra. Describes how the urinary tract works, why it’s important, what affects the amount of urine produced, and how to keep the urinary tract healthy.
Describes how the urinary tract works, why it’s important, what affects the amount of urine produced, and how to keep the urinary tract healthy.